Tobacco use in Michigan 2023
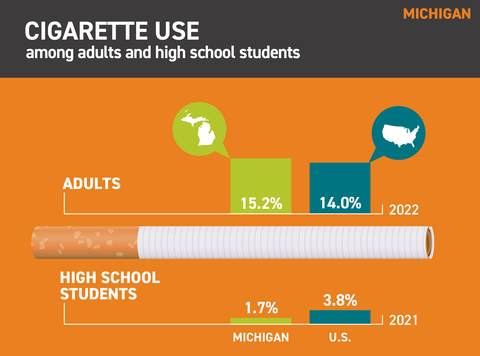
Cigarette use: Michigan*
Smoking rate in Michigan
- In 2022, 15.2% of adults in Michigan smoked. Nationally, adult smoking prevalence was 14.0%.1
- In 2021, 1.7% of high school students in Michigan smoked cigarettes on at least one day in the past 30 days. Nationally, smoking prevalence among high school students was 3.8%.2
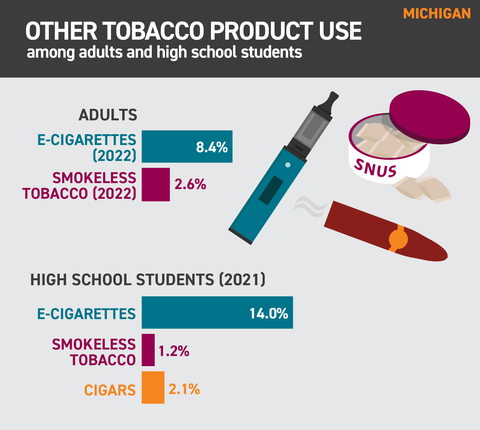
Other tobacco product use: Michigan*
Vaping rate in Michigan
- In 2022, 8.4% of adults in Michigan used e-cigarettes. Nationally, adult e-cigarette use prevalence was 7.7%1
- In 2022, 2.6% of adults in Michigan used smokeless tobacco every day or some days. Nationally, adult smokeless tobacco use prevalence was 3.4%1
- In 2021, 14.0% of high school students in Michigan used electronic vapor products on at least one day in the past 30 days. Nationally, e-cigarette use prevalence among high school students was 18%.2
- In 2021, 1.2% of high school students in Michigan used chewing tobacco, snuff or dip on at least one day in the past 30 days. Nationally, smokeless tobacco use prevalence among high school students was 2.5%.2
- In 2021, 2.1% of high school students in Michigan smoked cigars, cigarillos or little cigars on at least one day in the past 30 days. Nationally, cigar use prevalence among high school students was 3.1%.2
Economics of tobacco use and tobacco control
Tobacco taxes in Michigan
- Michigan received $ 1.2 billion (estimated) in revenue from tobacco settlement payments and taxes in fiscal year 2022.4
- Of this, the state allocated $1.8 million in state funds to tobacco prevention in fiscal year 2022, 1.7% of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s annual spending target.4
- Smoking-caused health care costs: $5.33 billion per year.4
- Smoking-caused losses in productivity: $11.5 billion per year.5
Michigan tobacco laws
Michigan tobacco laws
Tobacco taxes
- Michigan is ranked 19th in the U.S. for its cigarette tax of $2.00 per pack (enacted July 2004), compared to the national average of $1.93. (New York has the highest tax at $5.35 and Missouri has the lowest at 17 cents.)6-8
- Cigars are taxed 32% of the wholesale price. Non-cigarette smoking tobacco and smokeless tobacco are taxed 32% of the wholesale price.6,7
Clean indoor air ordinances
- Smoking is prohibited in all government workplaces, private workplaces, schools, childcare facilities, restaurants, bars (except in cigar bars), retail stores and recreational/cultural facilities.7
- Smoking restrictions are required in casinos/gaming establishments (tribal establishments are exempt).7
- The use of e-cigarettes is prohibited in the state’s Third Judicial Circuit Court, on streetcars and street railway stations, and on child care center property and in homes and vehicles used to transport children in care when in operation for child care.9
Licensing laws
- Wholesalers are required to obtain a license to sell tobacco products. Retailers are not required to obtain a license to sell tobacco products.6
- A license is not required to sell e-cigarette products.9
Youth access laws
- In December 2019, the United States adopted a law raising the federal minimum age of sale of all tobacco products to 21, effective immediately.
- Establishments are required to post signs stating that sales to minors are prohibited.6
- Minors are prohibited from buying vapor products and using them in a public place.9
- Internet sales of vapor products is permitted after verifying the purchaser is at least 18 years of age through a third-party service.9
Quitting statistics and benefits
Quitting smoking in Michigan
- The CDC estimates 51.2% of daily adult smokers in Michigan quit smoking for one or more days in 2019.3
- In 2014, the Affordable Care Act required that Medicaid programs cover all tobacco cessation medications.7**
- Michigan’s state quit line invests .66 cents per smoker, compared to the national median of $2.37.7
- Michigan does not have a private insurance mandate provision for cessation.7
Notes and references
Notes and references
Updated June 2023
* The datasets for both adults and youth prevalence were used to make direct comparisons at the state and national levels. National prevalence reported here may differ from what is reported in our national-level fact sheets. The numbers here also reflect the most recent data available. Dates of available data may differ across state fact sheets.
**The seven recommended cessation medications are NRT gum, NRT patch, NRT nasal spray, NRT inhaler, NRT lozenge, Varenicline (Chantix) and Bupropion (Zyban).
Fiore MC, et al. Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 Update. Clinical Practice Guideline. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services. Public Health Service: May 2008.
1. CDC, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2022.
2. CDC, Youth Risk Behavioral Surveillance System, 2021.
3. CDC, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, State Tobacco Activities Tracking and Evaluation System, 2021.
4. Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids, Broken Promises to Our Children: a State-by-State Look at the 1998 State Tobacco Settlement 24 Years Later FY2023, 2023.
5. Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids, Toll of Tobacco in the United States.
6. American Lung Association, State Legislated Actions on Tobacco Issues (SLATI).
7. American Lung Association, State of Tobacco Control, 2023.
8. Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids. State Cigarette Excise Tax Rates & Rankings. https://www.tobaccofreekids.org/assets/factsheets/0097.pdf. Accessed October 4th, 2023.
9. Public Health Law Center. U.S. E-Cigarette Regulation: 50-State Review. http://www.publichealthlawcenter.org/resources/us-e-cigarette-regulations-50-state-review. Accessed October 4th, 2023
More in smoking by region
Want support quitting? Join EX Program
By clicking JOIN, you agree to the Terms, Text Message Terms and Privacy Policy.
Msg&Data rates may apply; msgs are automated.